- FMA
- The Fabricator
- FABTECH
- Canadian Metalworking
Seco Tools uses 3D manufacturing to create new opportunities
- April 20, 2023
- News Release
- Cutting Tools
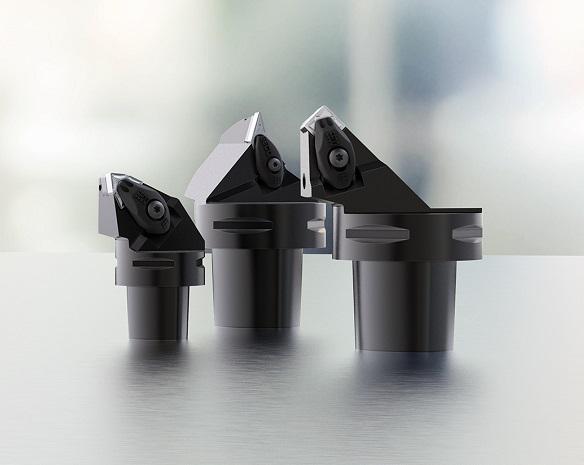
Seco Tools is using additive manufacturing (AM) or 3D printing to create products that would otherwise be difficult or impossible to manufacture. The advantages include shorter lead times, improved tool life, and increased sustainability.
The development and manufacture of prototypes for metal-cutting machining by means of AM is becoming increasingly commonplace in the operations of Seco Tools. One of the main strengths of this manufacturing method is the possibility of making specialized customer-specific tools that are difficult to achieve through conventional manufacturing.
AM technology will come into its own when producing tools that must be designed in a special way. This may involve complex geometries or other customizations to customer-specific needs.
Examples of such customizations include making the tools lighter, which improves the vibration-dampening properties, or provide them with better cooling possibilities.
“By directing the coolant to hit the cutting edge at just the right place, we can significantly extend the tool’s useful life," said Ingemar Bite, R&D specialist, Seco Tools. "With AM technology, coolant can be guided to locations that would otherwise have been impossible. AM allows for us to produce geometries that require less manufacturing steps, which often results in shorter lead times and thereby, faster deliveries.”
AM technology will also open up the possibility of repairing broken tools in the future, by removing dysfunctional components and printing them anew. This could, for example, involve tool components or the reuse of different types of machine-side connections. Also, compared with traditional manufacturing in this context, is that there is less waste of materials.
Seco Tools is already manufacturing cooling clamps for its Jetstream tools through 3D printing.
“The cooling clamps have a complex form with curved cooling channels and are thus well-suited to this type of manufacture,” said Bite.
Different methods can be used for additive manufacturing; the one that Seco Tools uses is called Selective Laser Melting (SLM), where lasers and a bed of metal powder are used to construct the products. In an SLM machine, a roughly 20–60 μm layer of powder is spread, and then processed by a laser. This process is repeated, layer by layer. Once all the layers are in place, the excess powder is removed and the product goes into post-processing for its final form.
subscribe now


Keep up to date with the latest news, events, and technology for all things metal from our pair of monthly magazines written specifically for Canadian manufacturers!
Start Your Free Subscription- Trending Articles
Automating additive manufacturing

Sustainability Analyzer Tool helps users measure and reduce carbon footprint
Sandvik Coromant hosts workforce development event empowering young women in manufacturing

GF Machining Solutions names managing director and head of market region North and Central Americas

Mitutoyo updates its end-user portal
- Industry Events
CTMA Economic Uncertainty: Helping You Navigate Kitchener Seminar
- May 2, 2024
- Kitchener, ON Canada
Automate 2024
- May 6 - 9, 2024
- Chicago, IL
ANCA Open House
- May 7 - 8, 2024
- Wixom, MI
17th annual Joint Open House
- May 8 - 9, 2024
- Oakville and Mississauga, ON Canada
MME Saskatoon
- May 28, 2024
- Saskatoon, SK Canada















